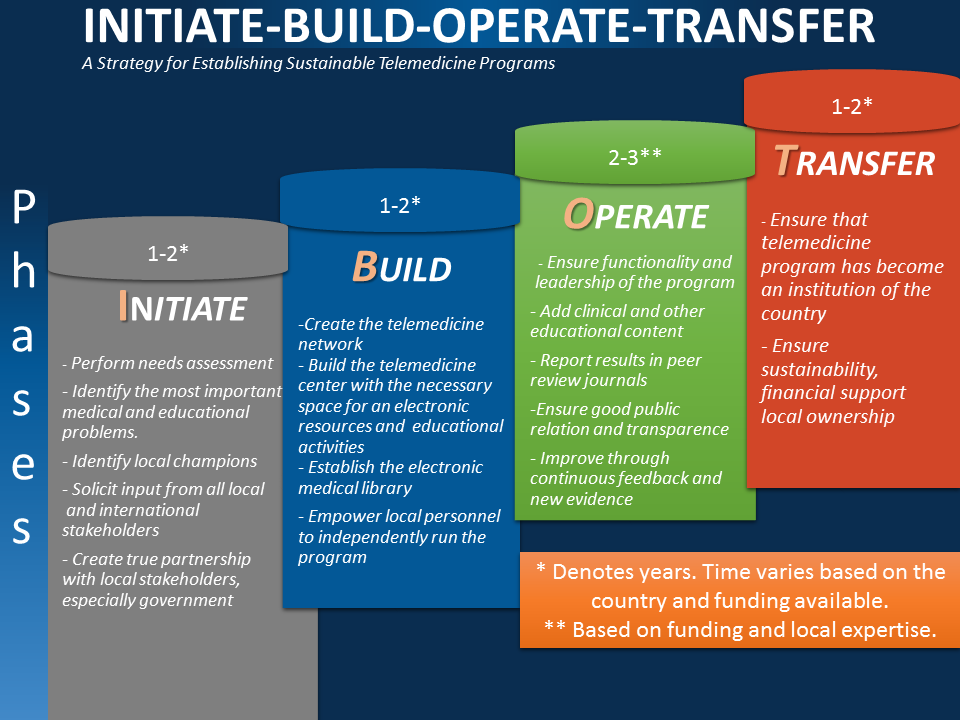
The Initiate-Build-Operate-Transfer (IBOT) strategy is the main model of project implementation model of International Virtual e-Hospital Foundation to ensure sustainability of activities. It involves a structured approach to starting a project, building and operating it, and eventually transferring ownership or control of the project to another party, often the public sector or government. Here’s an overview of the IVeH IBOT strategy.
- Initiate: In this phase, the IVeH, in partnership with other organizations (academia, foundations, agencies) or governments, identifies a project opportunity and initiates the development process. This involves conducting feasibility studies, securing necessary permits and approvals, and engaging with stakeholders such as the government, donors and local communities.
- Build: Once the project is initiated and accepted by stakeholders, the IVeH initiates implementation and development of the project. This includes project design, engineering, procurement, construction, build human capacities to ensure local and country-wide or region-wide sustainable expertise and other commissioning activities.
- Operate: After the project is completed and operational, the established institution or entity operates and manages the project as per the agreed terms and conditions. This could involve providing ongoing maintenance, managing operations, ensuring service delivery, and generating revenue., and ensure full reporting and transparency.
- Transfer: The final phase involves transferring ownership, control, or operation of the project to the public sector or another designated entity, assigned by the government. This could be the government, a public agency, or a combination of stakeholders. The transfer can include the physical assets, operational responsibilities, and sometimes contractual arrangements associated with the project. The transfer usually occurs at a predetermined time or after specific conditions are met, such as achieving performance targets or a set period of operation.
The IBOT strategy offers several potential benefits. It allows private sector entities to participate in infrastructure development while sharing risks with the public sector. It provides financial resources and expertise for project implementation, promotes technology transfer, and can help expedite infrastructure development. Furthermore, the strategy enables the public sector to benefit from private sector efficiency, innovation, and project management capabilities.
However, it is important to note that the success of the IBOT strategy depends on various factors, such as the proper structuring of contracts, effective risk allocation, transparent governance mechanisms, and clear objectives. Additionally, each project and its implementation may have unique considerations and challenges that need to be addressed on a case-by-case basis.
It is advisable to consult with professionals specializing in project management, finance, and legal matters, as well as local regulations and policies, to ensure the successful implementation of the IBOT strategy for a specific project or industry context.
- Latifi R. “Initiate-build-operate-transfer” – a strategy for establishing sustainable telemedicine programs not only in the developing countries. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2011;165:3-10. PMID: 21685579.
- Latifi R, Merrell RC, Doarn CR, Hadeed GJ, Bekteshi F, Lecaj I, Boucha K, Hajdari F, Hoxha A, Koshi D, de Leonni Stanonik M, Berisha B, Novoberdaliu K, Imeri A, Weinstein RS. “Initiate-build-operate-transfer”–a strategy for establishing sustainable telemedicine programs in developing countries: initial lessons from the balkans. Telemed J E Health. 2009
- Latifi R, Dasho E, Lecaj I, Latifi K, Bekteshi F, Hadeed M, Doarn CR, Merrell RC. Beyond “Initiate-Build-Operate-Transfer” strategy for creating sustainable telemedicine programs: lesson from the first decade. Telemed J E Health. 2012 Jun;18(5):388-90. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2011.0263. Epub 2012 Apr 23. PMID: 22524525.