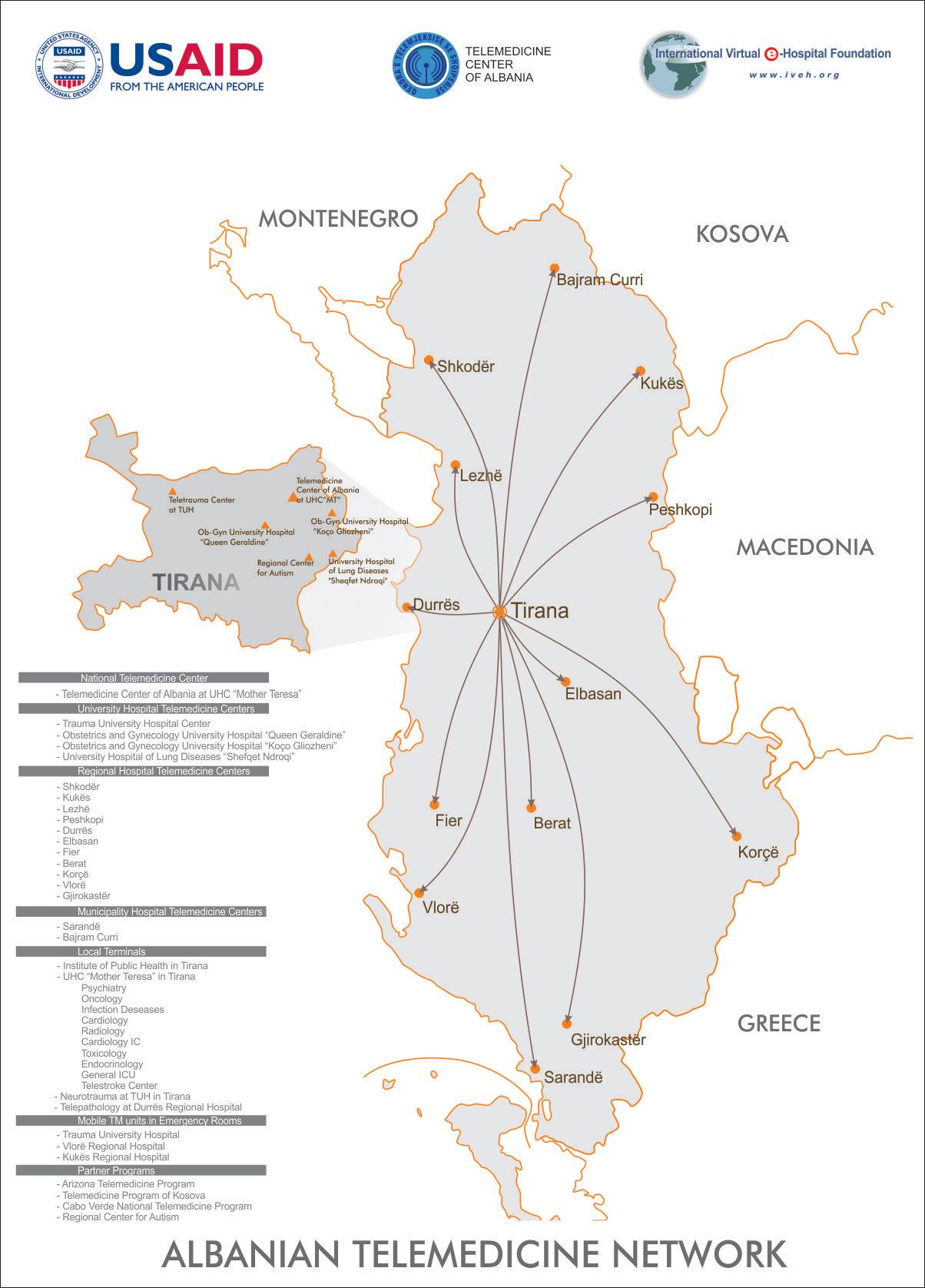
The Integrated Telemedicine and e-Health program (ITeHP) of Albania, built by the International Virtual e-Hospital Foundation (IVeH), has improved access to high-quality healthcare, particularly in high demanding specialty disciplines. The telemedicine program in Albania has improved access to specialized care in a number of specialty clinical disciplines, particularly in potentially life-threatening and time-sensitive conditions such as neurotrauma.
Albania has increasingly embraced telemedicine as a means to improve healthcare accessibility and delivery across the country. Here are some key aspects of the telemedicine program in Albania:
- Teleconsultations: Teleconsultations form a significant part of Albania’s telemedicine program. Through videoconferencing or virtual communication platforms, patients can remotely consult with healthcare professionals, seek medical advice, receive prescriptions, and discuss their health concerns. This approach is particularly beneficial for patients in rural or remote areas who may have limited access to healthcare facilities.
- National Telemedicine Network: Albania has been developing a National Telemedicine Network to facilitate the seamless exchange of medical information and teleconsultations between healthcare providers. This network connects various healthcare facilities, including hospitals, clinics, and primary care centers. It aims to improve coordination and ensure that patients receive medical attention regardless of their geographical location.
- Specialist Referrals: Telemedicine allows for easier and faster access to specialist care. General practitioners or primary care physicians can consult remotely with specialists for guidance and expertise. This collaboration ensures that patients receive timely and appropriate care without requiring extensive travel or waiting times.
- Patient Monitoring: Telemedicine programs in Albania also include remote patient monitoring. This involves utilizing digital health technologies to monitor patients’ vital signs, such as blood pressure, heart rate, and glucose levels, from their homes. This helps healthcare providers monitor and manage chronic conditions, reducing the need for frequent in-person visits.
- Training and Capacity Building: The successful implementation of telemedicine relies on healthcare professionals’ understanding and competence in using relevant technologies. Therefore, training programs and capacity-building initiatives have been organized in Albania to educate healthcare providers, enhance their telemedicine skills, and ensure effective utilization of telemedicine resources.
- Legal and Regulatory Framework: Albania has been actively working on establishing a legal and regulatory framework for telemedicine. This includes addressing issues related to privacy, data protection, licensing, and reimbursement. Clear guidelines and regulations provide a structured environment for the practice of telemedicine, ensuring patient safety and data security.
It’s important to note that the specific details and scope of the telemedicine program in Albania may evolve and vary over time. For the most accurate and up-to-date information on Albania’s telemedicine initiatives, it is advisable to refer to official sources such as the Ministry of Health or local healthcare providers involved in telemedicine services.